DeXgine - Module Types
DeXgine provides several module types for structuring the user interface
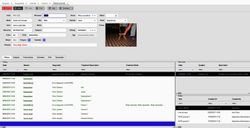
List
The list module provides a tabular display of multiple records, organizing the data with one row per record and one column per displayed attribute.
The list offers comprehensive CRUD functionality, allowing users to view (select), add (insert), modify (update), and delete records.
This functionality allows for flexible control over these operations, enabling or disabling them based on defined conditions during design or run-time.
Lists provide a flexible solution for a variety of needs:
- Report modules are designed solely for displaying multiple records retrieved from the database.
- When defining this module, do not add the Insert, Delete, Save, and Undo buttons. If these buttons were automatically generated from the table definition, remove them.
- Selecting the read only option will make the displayed information non-editable, preventing users from modifying it.
- Data Operator mode provides full access to the displayed data class, allowing you to enable all four standard operations (CRUD) or select a subset of them.
- Add the Insert, Delete, Save, and Undo buttons to the module. If you used automatic generation from the table definition, these buttons may already be included.
- If you do not require any special processing for these buttons, simply leave their other attributes blank. The deXgine runtime environment will automatically populate these attributes during the module build process.
- Master-Detail mode. If your data display includes a large number of columns, the master-detail mode is recommended. This mode eliminates the need for horizontal scrolling, making it easier for users to find and edit data.
- A list module, configured in a 'Master-Detail' style, is used to display records and facilitate the process of finding specific records of interest.
- Double-clicking a record triggers the opening of a detail module, which provides the ability to perform insert, update, and delete operations on that record.
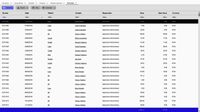
Detail
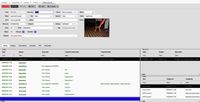
The detail module enables users to perform select, insert, update, and delete operations on individual records.
The information is presented in the form of discrete fields (of type edit, combo, check-box, date, date-time, file or picture).
Field placement on the screen is determined by the DeXgine runtime, based on the information in the layout definition matrix. This depends on:
- Field dimension
- The selected language (due to varying field label lengths).
- The user's chosen font.
Tree
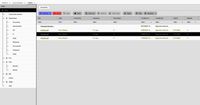
The tree module supports CRUD operations on hierarchical data (parent-child relationships).
The tree module is designed to manage tree structures having one or more root node(s).
Calendar
The calendar module allows users to view and modify information presented in a calendar format. This module is applicable to data categories that are naturally visualized as calendars, such as activity calendars, resource or people allocations, and similar data.
The calendar offers multiple data display options.
- 1 day
- 3 days
- 1 week
- 1 month
- 1 day with multiple resources (for multi-resource calendars)
Chart
The chart module facilitates the graphical representation of information, thereby supporting Business Intelligence functionalities.
It provides multiple options for displaying data.
- Column
- Bar
- Line
- Line (smooth)
- Area
And, can also display a series of indicators:
- Standard Deviation
- Simple Moving Average
- Exponential Moving Average
- Bollinger Bands
- RSI
- MACD
- Parabolic SAR
This module functions with a reporting cube table that has N axes and K values.
The cube can be defined manually or automatically generated by deXgine Developer based on the table definition.
Work Area
The Work Area module functions as a splitter, allowing the application window to be divided into multiple independent work areas. Within each of these work areas, different modules can be loaded and used independently.
COM-PLUGIN
In some cases, the interface provided by the deXgine runtime may not be adequate for implementing complex functionalities, such as integration with Geographic Information Systems (GIS).
For complex integrations, a COM-Plugin module serves as a host for an external COM component that you develop. This external COM component is responsible for handling the specific functionality and must implement the IXGModulePlugin interface for seamless integration.